NKF KDOQI GUIDELINES
KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Managing Dyslipidemias in Chronic Kidney Disease
Research Recommendations
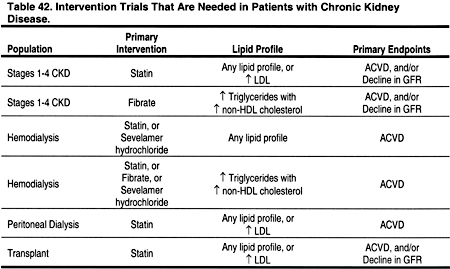
THERE ARE REASONABLE doubts as to whether trial results from the general population are applicable to all patients with CKD. It is beyond the scope of these guidelines to recommend all research that should be conducted in patients with dyslipidemia and CKD, or to design clinical trials. However, it is apparent that some questions are particularly well suited for study (Table 42), although these recommendations are not meant to be endorsements for specific protocols.
For children with CKD and/or a functioning kidney transplant, prospective cohort studies with long-term follow-up are recommended to determine:
- The prevalence of dyslipidemias at all stages of CKD over time
- The associations between dyslipidemias and subsequent ACVD
For children with CKD and/or a functioning kidney transplant, phase I and phase II trials, and pharmacokinetic dosing studies are recommended to establish the safety and lipid-lowering efficacy of agents (including, but not limited to):
- Bile acid sequestrants, eg, colesevelam
- Cholesterol uptake inhibitors, eg, ezetibmide
- Statins
- Fibrates
- Nicotinic acid
- Sevelamer hydrochloride
- Appropriate lipid-lowering drug combinations
For adults with CKD and/or a functioning kidney transplant, phase I and phase II trials and pharmacokinetic dosing studies are recommended to establish the safety and lipid-lowering efficacy of new agents (including, but not limited to):
- Colesevelam
- Cholesterol uptake inhibitors, eg, ezetimibe
- Appropriate lipid-lowering drug combinations
For patients with Stages 1-4 CKD, these and other appropriate studies are recommended to determine whether:
- A statin safely reduces the incidence of ACVD and all-cause mortality in patients with any lipid profile.
- A statin safely reduces the rate of decline in GFR in patients with any lipid profile.
- A statin safely reduces the incidence of ACVD and all-cause mortality in patients with LDL ≥100 mg/dL (≥2.59 mmol/L).
- A statin safely reduces the rate of decline in GFR in patients with LDL ≥100 mg/dL (≥2.59 mmol/L).
- A fibrate safely reduces the incidence of ACVD and all-cause mortality in patients with triglycerides ≥200 mg/dL (≥2.26 mmol/L) and non-HDL cholesterol ≥130 mg/dL (≥3.36 mmol/L).
- A fibrate safely reduces the rate of decline in GFR in patients with triglycerides ≥200 mg/dL (≥2.26 mmol/L) and non-HDL cholesterol ≥130 mg/dL (≥3.36 mmol/L).
For chronic hemodialysis patients, these and other appropriate studies are recommended to determine whether:
- A statin safely reduces the incidence of ACVD and all-cause mortality in patients with any lipid profile.
- A statin safely reduces the incidence of ACVD and all-cause mortality in patients with triglycerides ≥200 mg/dL (≥2.26 mmol/L) and non-HDL cholesterol ≥130 mg/dL (≥3.36 mmol/L).
- A fibrate safely reduces the incidence of ACVD and all-cause mortality in patients with triglycerides ≥200 mg/dL (≥2.26 mmol/L) and non-HDL cholesterol ≥130 mg/dL (≥3.36 mmol/L).
- Sevelamer hydrochloride safely reduces the incidence of ACVD and all-cause mortality in patients with triglycerides ≥200 mg/dL (≥2.26 mmol/L) and non-HDL cholesterol ≥130 mg/dL (≥3.36 mmol/L).
Click on Image to view full size
For chronic peritoneal dialysis patients, these and other appropriate studies are recommended to determine whether:
- A statin safely reduces the incidence of ACVD and all-cause mortality in patients with any lipid profile.
- A statin safely reduces the incidence of ACVD and all-cause mortality in patients with LDL ≥100 mg/dL (≥2.59 mmol/L).
For kidney transplant recipients, these and other appropriate studies are recommended to determine whether:
- A statin safely reduces the incidence of ACVD and all-cause mortality in patients with any lipid profile.
- A statin safely reduces the rate of decline in GFR in patients with any lipid profile.
- A statin safely reduces the incidence of ACVD and all-cause mortality in patients with LDL ≥100 mg/dL (≥2.59 mmol/L).
- A statin safely reduces the rate of decline in GFR in patients with LDL ≥100 mg/dL (≥2.59 mmol/L).

