NKF KDOQI GUIDELINES
KDOQI Clinical Practice Guidelines for Bone Metabolism and Disease in Children With Chronic Kidney Disease
Afterword
Since the time of our last committee meetings, long and frequent telecommunications, and late-night E-mail communiqués, additional drugs have become available for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism and hyperphosphatemia that will have an impact in the field of renal osteodystrophy in children with chronic kidney disease. We would like to highlight such developments and suggest that the next group of experts who reviews the care of pediatric osteodystrophy will be forthcoming with guidelines about these subjects.
Vitamin D Analogues
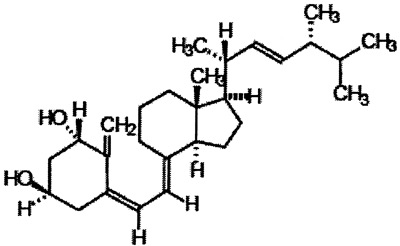
- Doxercalciferol (Hectorol®, Bone Care International R, Madison, WI) was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of osteodystrophy in adult patients with chronic kidney disease stages 2-5, in April 2004. Oral soft gelatin formulations (2.5 mcg; 0.5 mcg) and a parenteral formulation (2 mcg/mL) are available. Its structure is shown below:
Doxercalciferol acts as a pro-hormone, needing 25-hydroxylation in the liver for bioactivation into 1α, 25-hydroxyvitamin D2. Pivotal studies in adults on dialysis have demonstrated control of secondary hyperparathyroidism that is superior to placebo therapy, without undue suppression of 1st IMA-PTH < 300 pg/mL, or occurrences of hypercalcemia. Doxercalciferol has been shown to be effective in controlling secondary hyperparathyroidism of adult patients with CKD stages 3-4.
Use in children is not yet FDA approved, but recent data demonstrated that oral doxercalciferol given thrice-weekly is as effective as calcitriol in reducing PTH levels and improving the skeletal lesions of secondary hyperparathyroidism in children treated with peritoneal dialysis.163a
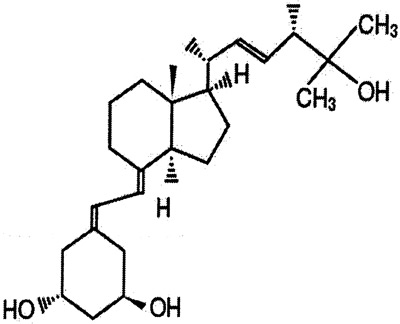
- Paricalcitol (Zemplar®, or 19-nor-1α, 25-dihydroxvitamin D3, Abbot Laboratories, Chicago, IL) has been available as a parenteral formulation for some time for patients with CKD stage 5, and is now available as 1-4 micrograms tablets. Its structure is shown below.
Paricalcitol is a synthetic, biologically active vitamin D analog of calcitriol with modification to the side chain (D2) and the A (19-nor) ring. Its biological actions are mediated through binding of the vitamin D receptor, which results in selective activation of vitamin D-responsive pathways. Paricalcitol has been shown to reduce 1st IMA-PTH by inhibiting PTH synthesis and secretion in adult patients undergoing maintenance hemodialysis.321 Use in children remains unpublished.
Calcimimetic Agents
Cinacalcet hydrochloride (Sensipar®, Amgen, Thousand Oaks, CA) is a calcimimetic, the first of a new class of pharmacologic agents that modulate the actions of the membrane-anchored calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) located on the parathyroid cells. The CaSR is also located in the kidney tubules, as well as many other cells within the body. Activation of the CaSR, whether by calcium or by a calcimimetic agent, reduces PTH secretion. The reduction in PTH diminishes bone resorption and is thus associated with a concomitant decrease in serum calcium and phosphorus levels.
Its structure is shown below.
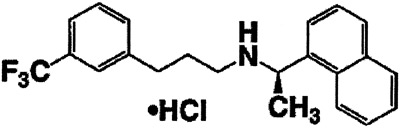
Cinacalcet hydrochloride has been approved for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism of stage 5 CKD (maintenance dialysis) in adults. Its pharmacokinetics are being studied in children on maintenance dialysis, but no data are yet available. At present, there is no recommendation regarding the use of cinacalcet hydrochloride in children with CKD. As the CaSR is expressed at the level of the growth plate, the safety of cinacalcet hydrochloride in growing children remains to be demonstrated.
Phosphate Binder
Lanthanum carbonate (Fosrenol®, Shire US Inc., Wayne, PA) contains lanthanum carbonate (2:3) hydrate with a molecular formula of La2(CO3)3 xH2O (on average, x=4-5) and serves as a dietary phosphate binder. Lanthanum carbonate inhibits absorption of phosphate by forming highly insoluble lanthanum-phosphate complexes and thereby reduces both serum phosphorus and the Ca X P product in patients with CKD.
In 105 adults with kidney failure treated with lanthanum carbonate for up to 4-5 years, rising levels of lanthanum were noted over time. Estimates of elimination half-life from bone ranged from 2-3.6 years. Steady-state bone concentrations were not reached during the period studied.
There are no studies in children on maintenance dialysis. Further, the current FDA-approved label for lanthanum carbonate indicates that lanthanum can be found in the growth plate.557 Therefore, we do not recommend use of lanthanum carbonate for the chronic treatment of hyperphosphatemia in children.